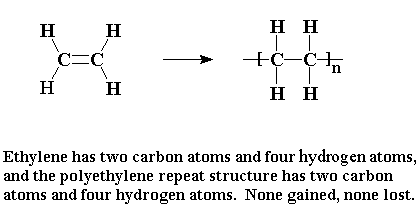What Is Addition Polymerization Explain With Example
Schematic representation of addition polymerization is presented in Fig. Alkenes are the monomers.
Carboxylic Acids Easy Exam Revision Notes For Gsce Chemistry
Schematic representation of addition polymerization is presented in Fig.

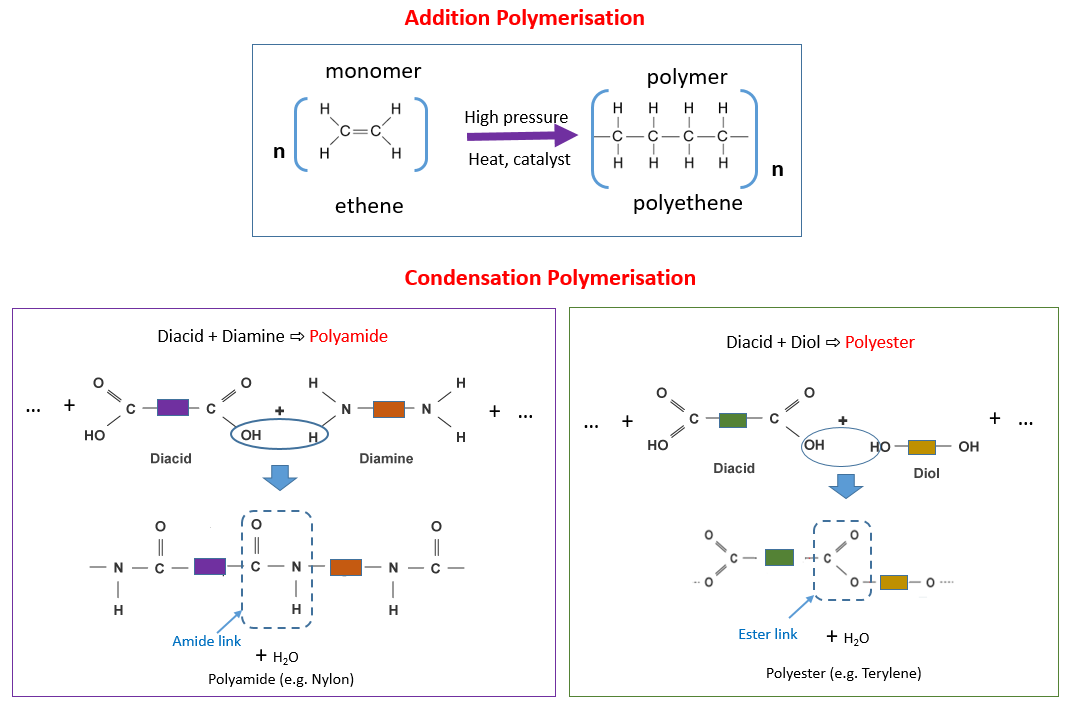
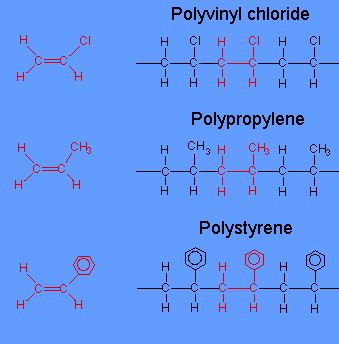
What is addition polymerization explain with example. The name of the polymer is deduced by putting the name of the monomer in brackets and adding poly- as the prefix. Common examples of addition polymerization are polyethylene polyvinyl chloride PVC acrylics polystyrene polytetrafluoroethylene and polyoxymethylene acetal. Polymerisation is the process wherein alkene monomers are joined together into long polymer chains.
In addition polymerization monomers react to form a polymer without the formation of by-products. The double bonds are broken and linked with each other to form a long chain polymer. For an example we will take the synthesis of polyethylene which is an addition polymer useful in making products such as garbage bags food wrap jugs etc.
An addition polymer is a polymer that forms by simple linking of monomers without the co-generation of other products. During the addition polymerization all monomers are consumed and no byproducts are formed. C C F 2.
Poly ethene is the polymer The CC double bond in ethene is involved in the polymerisation reaction. In addition polymerisation monomers have multiple. Its repeating unit is CH 2 -.
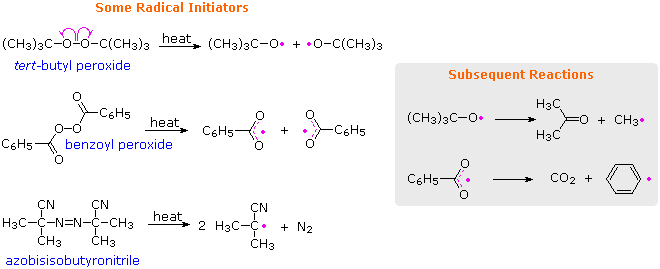
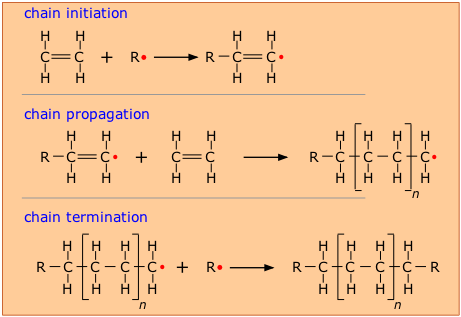
A polymer formed by direct addition of repeated monomer molecules possessing double or triple bond without the elimination of any small molecule is called addition polymerisation. The three steps of this reaction to focus on are how the reaction gets started INITIATION. They are also known as chain growth polymers.
The formation of a polymer by addition polymerization is an example of a chain reaction. Addition polymerizations usually are carried out in the presence of catalysts which in certain cases exert control over structural details that have important effects on. Addition polymerization differs from condensation polymerization which does co-generate a product usually water.
Common examples of addition polymerization are polyethylene polyvinyl chloride PVC acrylics polystyrene polytetrafluoroethylene and polyoxymethylene acetal. Polythene is formed by the addition polymerisation of ethene monomers. These are mostly radical based polymerization for those monomers with double bonds.
For example if propene is the alkene monomer used then the name is polypropene. Lewis acids or bases radical initiators are catalysts in addition polymerization. Addition Polymerization Polymerization that occurs through the coupling of monomers using their multiple bonds is called addition polymerization.
In the initiation step a peroxide radical generates. During the addition polymerization all monomers are consumed and no byproducts are formed. The simplest example involves the formation of.
Examples include orlon teflon PVC polyethylene etc. All atoms of monomer are present in the polymer. The opposite of cracking breaking polymer chains down into monomers the double carbon bond is broken and the alkene becomes saturated with hydrogen forming.
The best example is polymerization of ethylene. Once a chain reaction gets started it is able to keep itself going. It allows ethene molecules to join together to form a single product so it is an example of.
Addition polymerizations usually are carried out in the presence of catalysts which in certain cases exert control over structural details that have important effects on the properties of the polymer. Normally addition polymerization means that two monomers react with each other and no other small molecules are generaged. Tetrafluoroethylene monomer nF 2.
Addition polymerisation is the chain growth process in which monomers of the same kinds undergo the addition of olefinic monomers. The monomer for polyethylene is ethene CH 2 CH 2. In polymerization In addition polymerization monomers react to form a polymer without the formation of by-products.
It is the process in which there is not the production of by-products.
9 17 Radical Chain Growth Polymerization Chemistry Libretexts

Polymerization Definition Classes Examples Britannica

10 2 Addition Polymerisation Sl Youtube

Addition Polymerization Youtube
10 3 Addition Polymerization One One One Gives One Chemistry Libretexts

Addition Polymerization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Addition Polymerization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Addition Polymer An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Polymerization Definition Classes Examples Britannica

What Is Polymerization Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
25 19 Polymerization Addition Polymers Chemistry Libretexts

Addition Polymerization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Condensation Polymers Examples Answers Activities Experiment Videos

Addition Polymerization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
12 Difference Between Additional And Condensation Polymerization With Examples Viva Differences

Addition Polymerization And Condensation Polymerization Hindi Youtube

Polymerization Definition Classes Examples Britannica

Addition Polymerization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics